Understanding the parts of a bathtub is a good practice for every homeowner, especially in the event of something going wrong. There are many parts to a bathtub that allows it to function correctly.
Here is an amazing custom 3D diagram we made about the main parts of a bathtub.
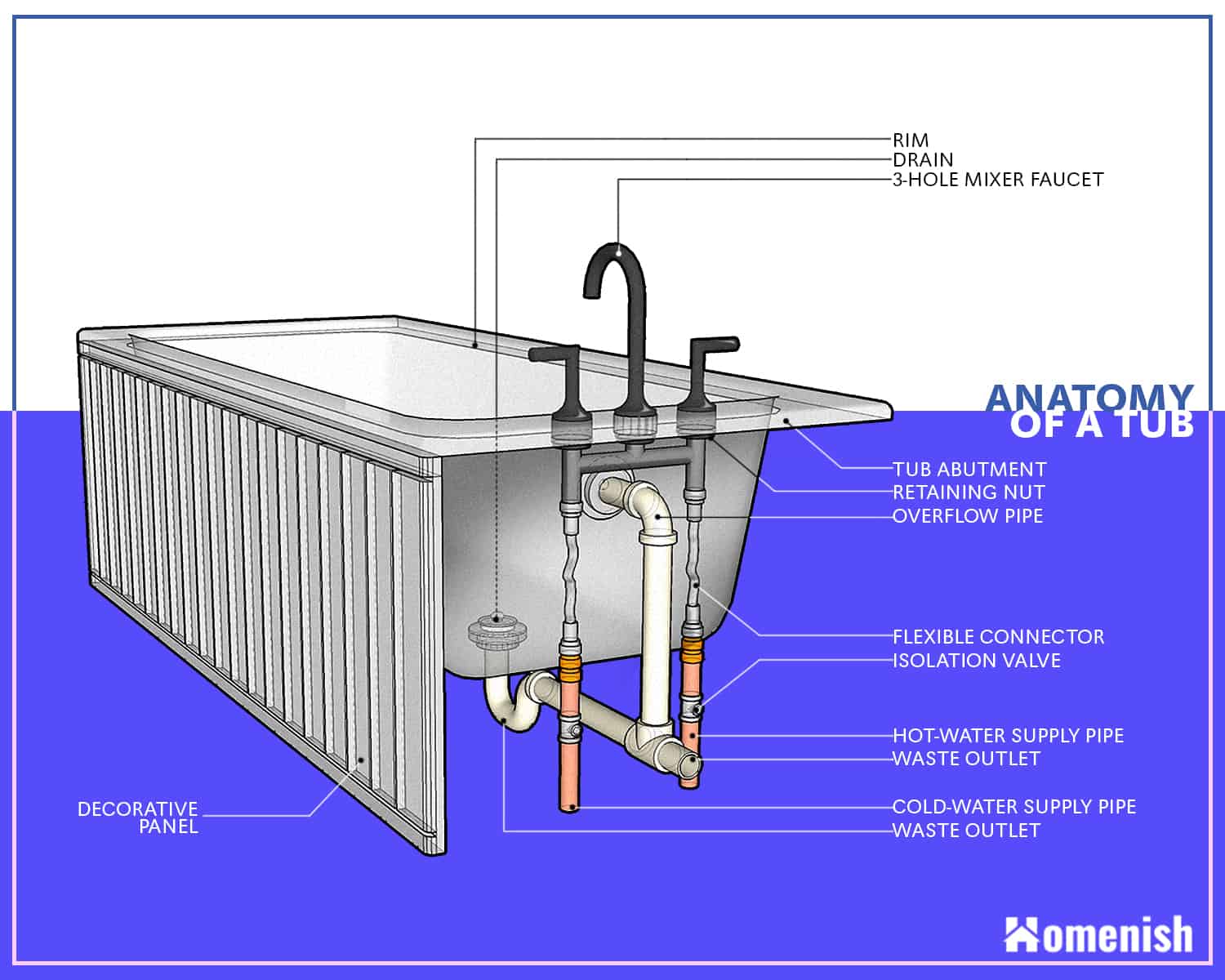
The Tub
The bathtub serves as a container for storing water when bathing. Tubs are either rectangular or oval. They have a central drain at the bottom that can be blocked to control water flow. Water is operated by faucets in most tubs, one for cold water and the other for heat. Newer bathtubs have thermostat mixing valves to ensure greater protection at higher temperatures. Tubs are a safe space to bathe young children. They also provide a cool relaxation space for adults after a long day’s job
Water Supply
The water supply ensures that water fills your bathtub whenever needed. It does this by supplying water to your faucets and showerhead peripherals. While turning on your water will give you a good indication of its overall purity, it is important to check your water supply for any damages or pollutants regularly. Coldwater is normally supplied either through a tower or a condenser, while warm water is typically supplied by your water heater. If you live in a house, the water source would be buried underground or installed in your basement or crawlspace so that you are not bothered by it in any way.
Shower
Your shower is directly attached to your water supply, and turning the showerhead would almost always have the water running out immediately. The size of your shower head could sometimes determine how much water flow you have coming in. You can reduce the size of your showerheads and replace them with more water-efficient models to save water. You may also increase them to have more water flow. But this would greatly increase the water bill. Your shower is operated by a series of control valves that separately control hot and cold water. Since there is no temperature regulator for the water in older models, you should be careful not to burn yourself; newer models, however, have thermostat mixing valves that prevent scalding.
Planar Cross
A planar cross is a four-cross link of pipes that controls water flow and is usually only used in bathtubs.
Shutoff Valves
Primary valves and fixture valves are the two kinds of shutoff valves that regulate the water flow to your house. Every fixture is supposed to have its stop valve to allow you to switch off the valve on any malfunctioning fixture. However, older fixtures may not have these individual valves, which means the central water supply would have to be turned off anytime there is a problem. If you notice that you have older model fixtures, you should consider installing newer ones.
Diverter Pipe
A diverter pipe is a piece of piping equipment that is used to divert water flow from a particular area or to centralize water flow to a particular point. It is often used to make cold and warm water come from the same faucet. They are used in nearly all appliances, including freestanding sinks, bathtubs. When you experience sudden low water pressure, always check your diverter pipes to see if they need replacement.
Drain
Everyone knows their bathtub drain because it gets blocked every so often. Bathroom drains are water outlets that let water out after you’re done having a bath. They often get blocked when hair or other dirt particles find their way into the drain.
Rim
The top edge of your tub is the rim. The rim’s purpose is to provide a stable base for your bathtub as well as a way to trap water that could leak out from the top when it’s filled to the brim.
Flexible Connector
There are several sizes and varieties of flexible connectors available in the market. A flexible connector’s job is to help connect two pipes that can’t connect. These connector pipes are normally made of braided steel and are adaptable to almost any home.
Overflow Pipe
The overflow pipe, which is located between your connectors and the drain, collects all of the excess water in your tub and directs it to your drain into a different pipe to lessen the load on your drain.
Waste Outlet
A waste outlet, also known as a drain-waste-vent, is a pipe that prevents waste products from getting into your water supply. Its job is to drag waste down to the drain, allowing it to be disposed of in its proper channel.
Trap
A trap is also called an S-bend because it’s made in the shape of the letter S laid sideways. Its job is to keep water trapped so that waste products from outside do not get into your home.
Decorative Panel
The decorative panel is the natural stones or tiles that conceal your bathroom’s internal pipe system. It aims to conceal much of the inner workings of the bathtub or sink from public view, resulting in a much nicer bathroom appearance.
Lining
The lining is the area of the wall on which the tub is secured. Water leaking from the tub into the lining could cause problems, which, if left untreated, will deteriorate with time.
Faucets
The primary function of a faucet is to provide water to the bathtub. These devices operate by restricting and allowing the flow of water in the pipes. The bathtub faucet can also regulate the temperature of the water that is released into the bathtub’s body. The parts of a facet include the lever and handle, cartridge, dome, and faucet spout.






